Gluteal Tendinopathy
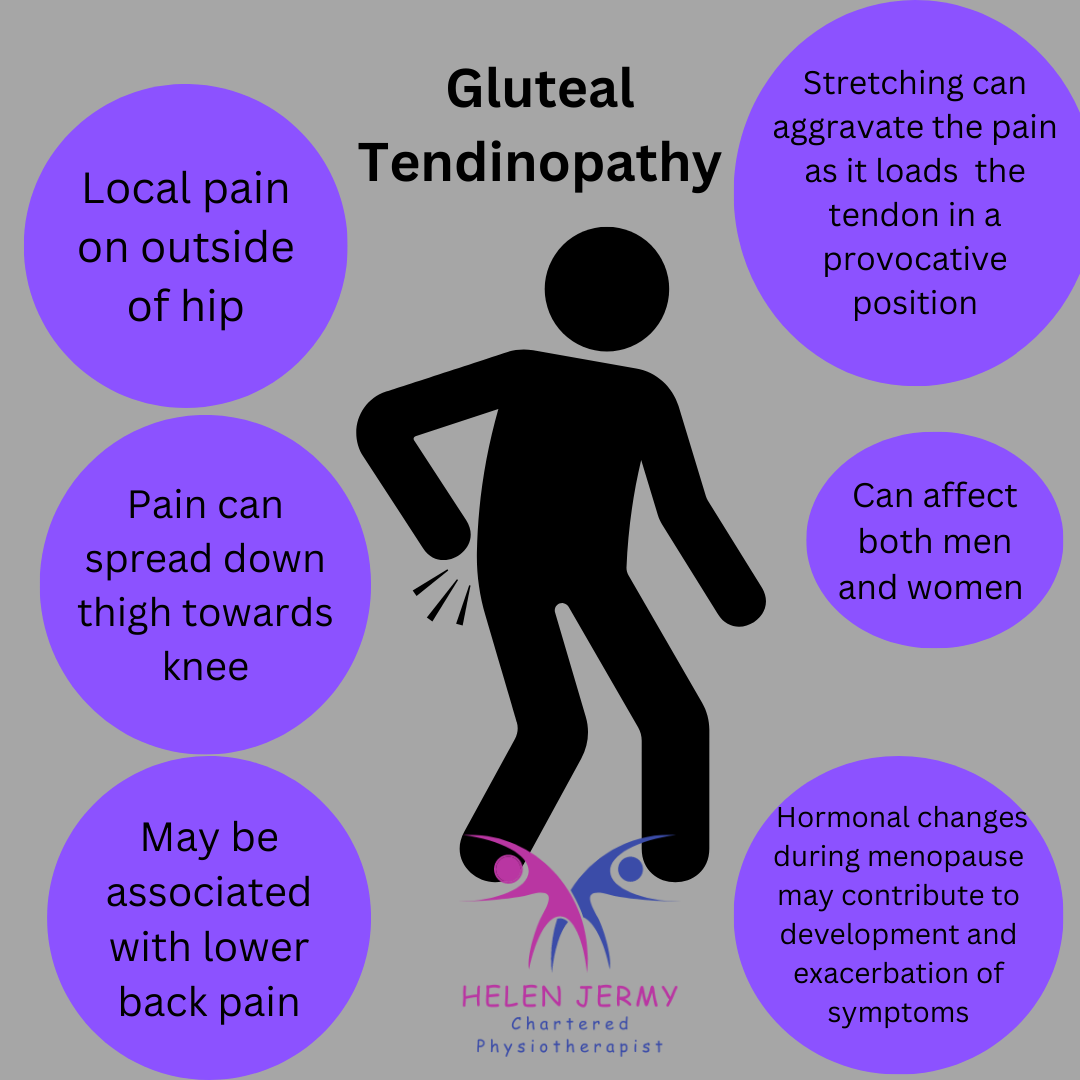
Gluteal tendinopathy, also known as gluteal tendonitis or gluteal tendinosis, is a condition that involves irritation, inflammation, and degeneration of the tendons in the gluteal muscles, particularly the gluteus medius and gluteus minimus tendons. These tendons are located in the buttock region and are responsible for various movements of the hip and thigh.
Common symptoms of gluteal tendinopathy may include:
- Pain: Patients often experience pain in the buttock or hip region. This pain can be sharp or aching and may worsen with activities like walking, climbing stairs, or standing on one leg.
- Tenderness: Tenderness and discomfort may be present when pressing on the outside of the hip, near the greater trochanter (the bony prominence of the thigh bone).
- Stiffness: Some people may experience stiffness in the hip and have difficulty moving it and with walking and climbing stairs.
- Weakness: Weakness in the hip or difficulty in maintaining single leg balance can also be associated with gluteal tendinopathy.
- Pain at night: Pain in the hip area may interfere with sleep, particularly when lying on the affected side.
Gluteal tendinopathy can affect both men and women, and there is some evidence to suggest that hormonal changes during menopause may play a role in the development or exacerbation of tendinopathy, as decreasing estrogen levels can impact the quality of tendons and their ability to repair.
The exact cause of gluteal tendinopathy can be multifactorial and is often associated with overuse, repetitive stress, or trauma to the gluteal tendons. It is more commonly seen in individuals who engage in activities that require repetitive hip movements, such as running, cycling, or dancing. Additionally, changes in biomechanics, muscle imbalances, and aging can contribute to the development of this condition.
Management of gluteal tendinopathy typically involves conservative treatments such as:
- Rest: Reducing or modifying activities that exacerbate symptoms.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can help with exercises to strengthen the gluteal muscles, improve hip stability, and address any biomechanical issues.
- Anti-inflammatory medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroid injections: In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Lifestyle modifications: Weight management, adjusting activities, footwear, or techniques to reduce stress on the affected tendons.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and to develop an appropriate treatment plan for gluteal tendinopathy based on your individual symptoms and needs, to maintain an active healthy lifestyle and to engage in appropriate exercise.
